查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过





Stroke & Vascular Neurology(SVN)最新上线文章“Group 2 innate lymphoid cells resolve neuroinflammation following cerebral ischaemia”,来自首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院、国家神经系统疾病临床医学研究中心金薇娜教授团队等。

急性脑缺血引起明显的炎症反应,进而加剧神经损伤。然而,对调控急性神经炎症消退的机制仍知之甚少。与调节性T细胞及调节性B细胞不同,2型固有淋巴细胞(group 2 innate lymphoid cells, ILC2s)是一种固有免疫调节细胞,可以在没有抗原呈递的情况下迅速动员。这些ILC2s是否参与及如何参与脑缺血后中枢神经系统炎症仍未可知。
研究团队利用缺血性卒中患者的脑组织和局灶性缺血小鼠模型,首先研究脑内ILC2s的存在、分布及其细胞因子释放。通过特异性抗体删除和ILC2s转输实验评估ILC2s对神经损伤的影响。使用接受IL-4−/−ILC2s被动转移的Rag2−/−γc−/−小鼠,研究者进一步评估了ILC2s释放的白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-4在缺血性脑损伤中的作用。
研究结果表明,ILC2s积聚于脑缺血患者脑组织的梗塞周围区域,以及局灶性脑缺血小鼠的脑组织中。少突胶质细胞通过分泌IL-33活化并动员ILC2s。ILC2s的过继转移和扩增减小梗死体积并改善神经功能缺损,其机制主要是通过释放IL-4以降低卒中损伤的严重程度。
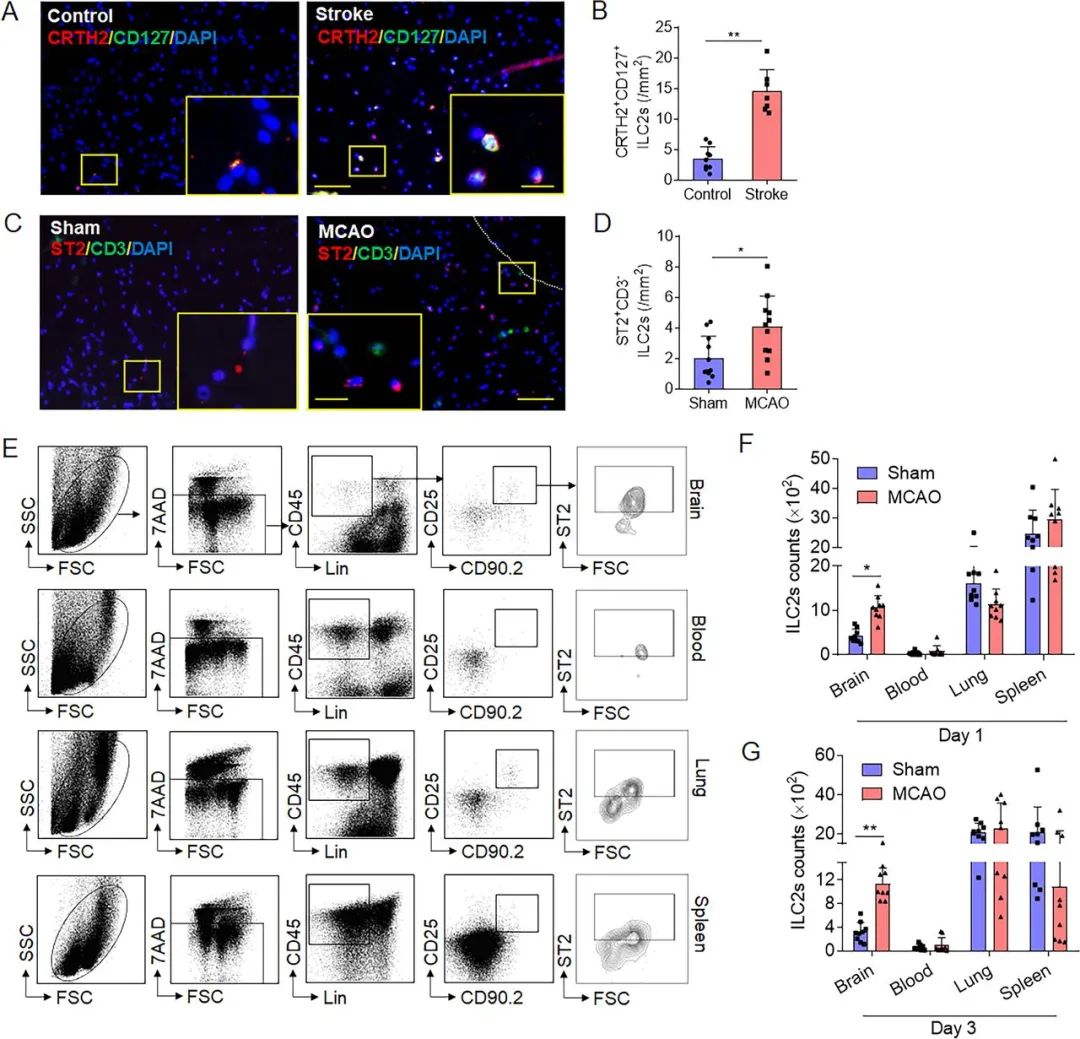
Figure 1. Brain infiltration of group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) following cerebral ischaemia. (A,B) ILC2s were counted in the brain tissue of healthy subjects (controls) and patients who had an ischaemic stroke during the early phase (<24 hours). Images and bar graphs show brain-infiltrating CRTH2+CD127+cells in brain sections obtained from patients who died of acute ischaemic stroke. Scale bar=50 µm (insert=20 µm). n=7 subjects (4 men and 3 women) in the stroke group; n=9 subjects (5 men and 4 women) in the control group. **p<0.01 according to Mann-Whitney test. (C,D) Male and female C57BL/6 (B6) mice were subjected to sham operation or middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The presence of ILC2s was evaluated in the brains of sham control or MCAO mice. Images and bar graph show brain-infiltratingCD3e−ST2+ILC2s from sham or MCAO mice. Scale bar=50 µm (insert=20 µm). n=11 mice per group. *p<0.05 according to two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (E) Flow cytometry plots show mouse ILC2s (Lin−CD45highCD90.2+ ST2+, Lin=CD3e, CD45R, CD11b, Ter119, Ly-6G, CD11c, NK1.1, CD4, CD5, CD8a, TCR-β and TCR-γδ) in the brain, peripheral blood, lung and spleen at day 1 after MCAO. (F,G) Summarised results show ILC2s numbers in the brain, peripheral blood, lung and spleen from sham or MCAO mice at day 1 and day 3 after MCAO. n=9 mice per group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 according to Mann-Whitney test. Data are presented as the mean±SD.
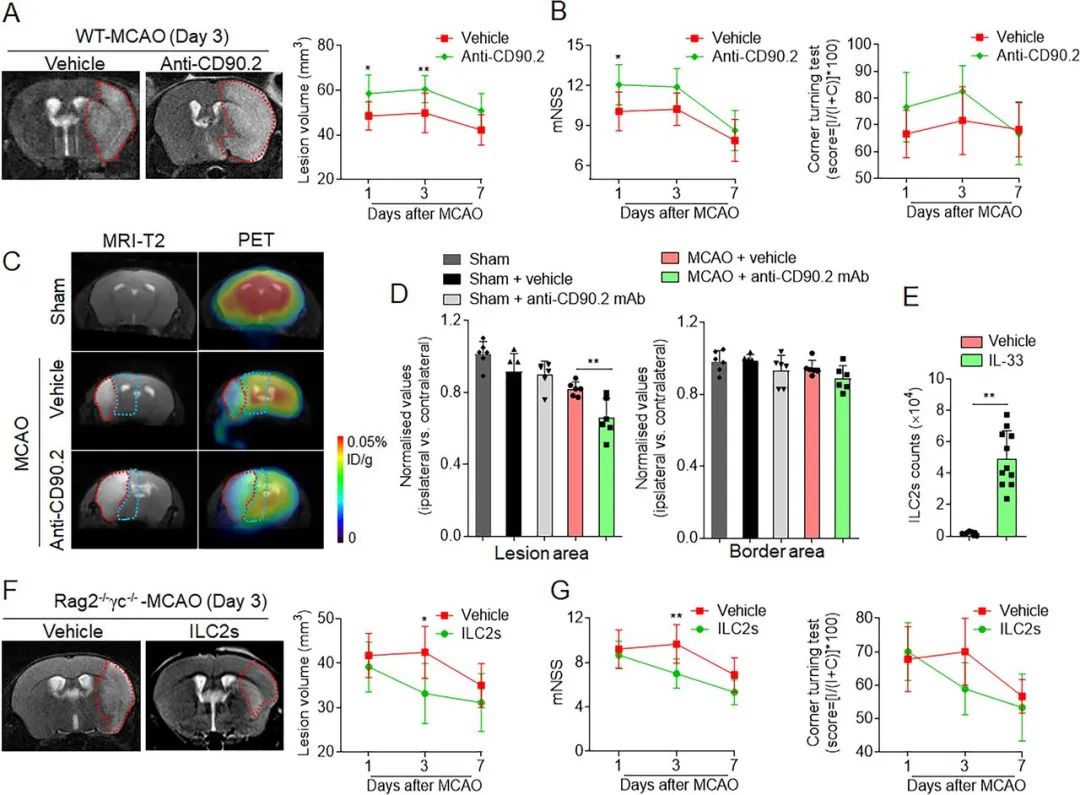
Figure 2. Effects of group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) on brain infarction and neurological deficits following cerebral ischaemia. (A,B) For antibody depletion, anti-CD90.2 mAb was treated by intravenous injection with a dose of 300 µg/mouse. Mice were treated with rat IgG2b as an isotype control immunoglobulin. The 7T-MRI and summarised results show the effects of antibody depletion of ILC2s on infarct volume (A) and neurological deficits (B) at the indicated time points (days 1, 3 and 7) after middle cerebral artery occlusion in wild-type mice (WT-MCAO). n=12. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 according to analysis of variance (ANOVA) test. (C,D) At day 3 after MCAO, metabolic variation in lesion core and border area of MCAO mice receiving antibody depletion of ILC2 were detected based on positron emission tomography (PET) scans. PET/CT images show [18F]-FDG activity. The radioactivity in the unaffected tissue was applied as the standard to normalise results from lesion core and border area of ipsilateral hemisphere. n=6. **p<0.01 according to ANOVA test for multiple comparisons at indicated time points. (E) To induce sufficient ILC2s, naïve C57BL/6 mice were challenged by intraperitoneal injection of recombinant IL-33 with condition of 600 ng/mouse for a total of 6 days. Spleens were collected to determine the IL-33-induced ILC2s number. n=12. **p<0.01 according to independent t-test. (F,G) A total of 1×106 purified ILC2s were isolated from splenocytes following in vivo IL-33 stimulation. Rag2−/−γc−/− mice received intravenous injection of ILC2s following MCAO and reperfusion. The 7T-MRI and summarised results show the effects of passive transfer of ILC2s on infarct volume and neurological deficits at days 1, 3 and 7 after MCAO. n=9. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 according to two-way ANOVA tests at indicated time points. Data are presented as the mean±SD.
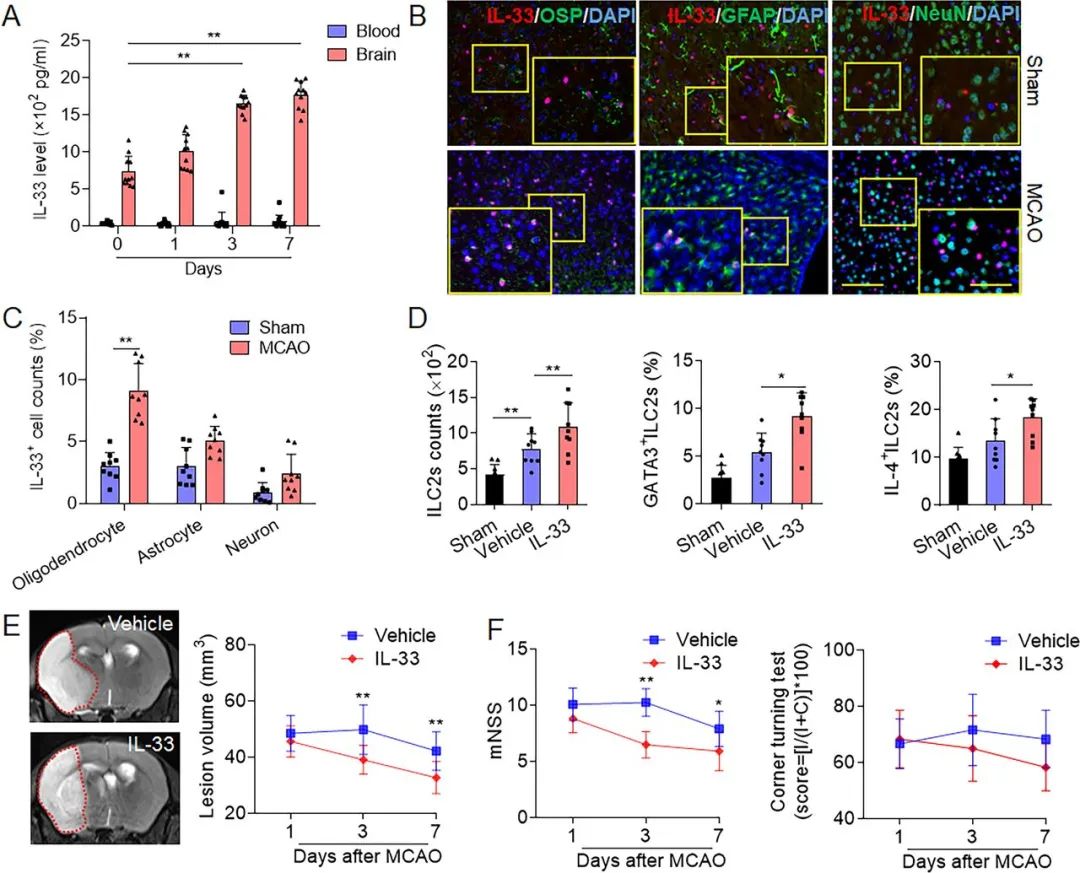
Figure 3. Oligodendrocytes express interleukin (IL-33) that expands group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and ameliorates ischaemic brain injury. (A) Brain tissues samples were collected from mice treated with sham operation or middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and reperfusion from 1 to 7 days. Measurement of IL-33 in brain homogenates and blood was conducted by an ELISA kit. n=11. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 according to independent t-test. (B) Immunostaining shows the indicated cell subsets (GFAP+, astrocytes; NeuN+, neurons; OSP+, oligodendrocytes) expressing IL-33 at day 1 after sham surgery. Scale bar=100 µm (inset=50 µm). (C) Quantification of immunostaining results shows IL-33-producing cells in brain tissues at day 1 after sham operation or MCAO. CD45−OSP+, oligodendrocytes; CD45−GFAP+, astrocytes; CD45−NeuN+, neurons; CD45intCD11b+, microglia; CD45−CD31+, endothelial cells. n=9. **p<0.01 according to Mann-Whitney test. (D) Brain tissues were collected from MCAO mice receiving intraperitoneal injection of IL-33. Flow cytometry analysis shows the number and activity of brain-infiltrating ILC2s in the indicated MCAO mice receiving IL-33 or vehicle (phosphate buffer saline, PBS). n=9. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 according to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test for multiple comparisons. (E) The 7T-MRI and summarised results show the effects of IL-33 injection on infarct volume at the indicated time points (days 1, 3 and 7) after MCAO. (F) The summarised results show the effects of IL-33 injection on neurological deficits after MCAO. n=12. **p<0.01 according to ANOVA test for multiple comparisons at indicated time points. Data are described by manner of mean±SD.
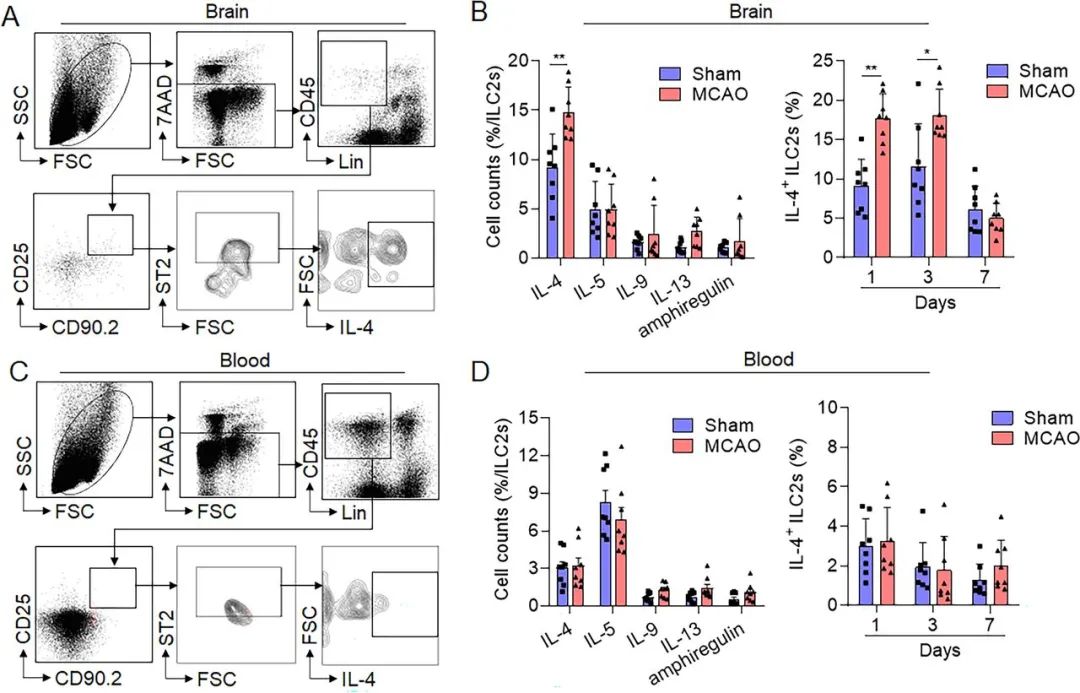
Figure 4. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s)-released cytokines in the brain and periphery blood following brain ischaemia. Male and female C57BL/6 (B6) mice were treated with sham surgery or middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). (A) Representative flow cytometry gating strategy showing interleukin (IL)-4-producing ILC2s in the mouse brain at day 1 after MCAO. Mouse ILC2s were identified as Lin−CD45highCD90.2+ ST2+. (B) Left panel, summarised results depict the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 and amphiregulin in ILC2s obtained from experimental animal brains at day 1 after MCAO or sham. Right panel, IL-4-producing ILC2s in the brain from day 1 to day 7 after MCAO or sham. n=8. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 according to Mann-Whitney test. (C) Typical flow cytometry gating strategy showing IL-4-producing ILC2s in mouse blood after MCAO surgery at day 1. Mouse ILC2s were identified as Lin−CD45highCD90.2+ ST2+. (D) Left panel, summarised results show the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 and amphiregulin in ILC2s obtained from mouse blood at day 1 post MCAO or sham. Right panel, IL-4-producing ILC2s in blood from day 1 to day 7 after MCAO or sham. n=8. Data are expressed as the mean±SD.
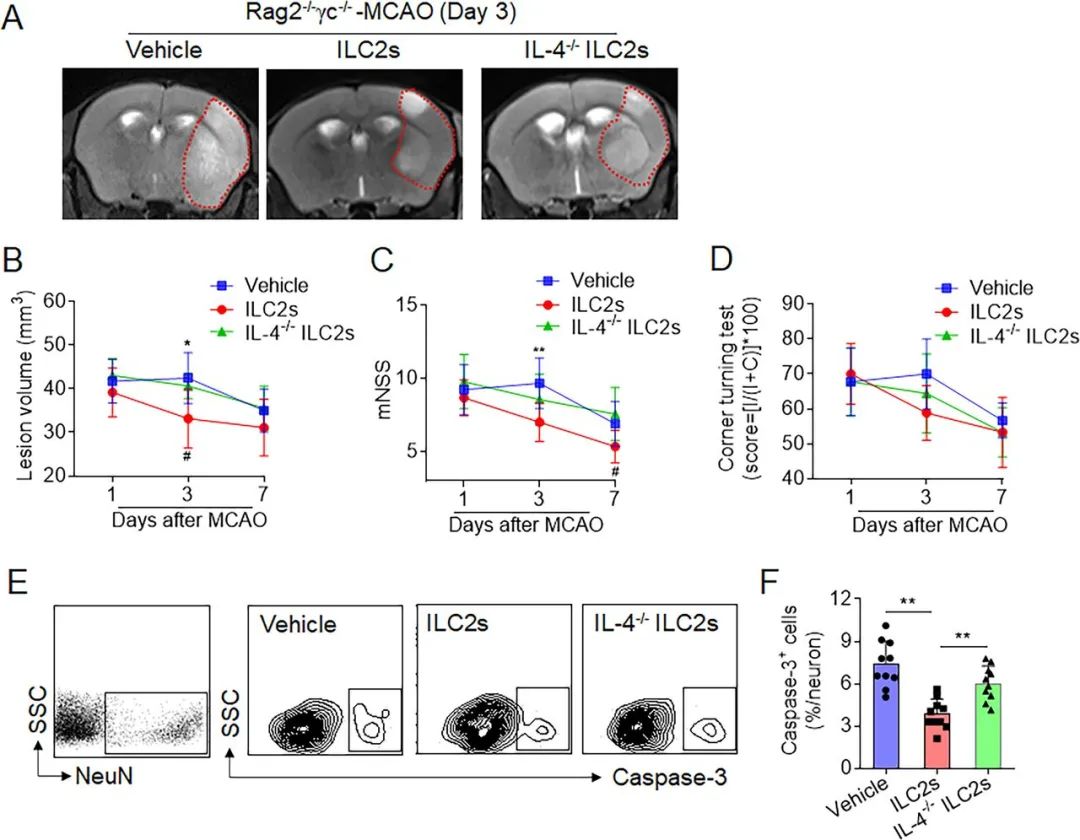
Figure 5. Effects of interleukin (IL)-4-producing group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) on brain injury following cerebral ischaemia. ILC2s were isolated from pooled splenocytes of wild-type C57BL/6 or IL-4−/− mice. Groups of Rag2−/−γc−/− mice were received intravenous injection of vehicle (phosphate buffer saline, PBS), wild-type ILC2s or IL-4−/−ILC2s followed by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The 7T-MRI and summarised results show infarct volume (A,B) and neurological function (C,D) in groups of Rag2−/−γc−/− mice (cell culture medium), wild-type ILC2s or IL-4−/−ILC2s at day 1, 3 and 7 after MCAO. n=9. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 according to analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the comparison of vehicle versus ILC2s at indicated time points; #p<0.05 according to ANOVA for the comparison of ILC2s versus IL-4−/−ILC2s at indicated time points. (E,F) Representative flow cytometry gating strategy and quantification showing Caspase-3 expression in neuronal cells, in groups of Rag2−/−γc−/− mice receiving vehicle (cell culture medium), wild-type ILC2s or IL-4−/−ILC2s at the indicated time points after MCAO.n=12. **p<0.01 according to two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. Data are presented as the mean±SD.
研究结论,脑缺血可通过动员ILC2s抑制神经炎症及脑损伤,扩展了目前对卒中后炎症进展机制的理解。

来源:SVN俱乐部
转载已获授权,其他账号转载请联系原账号
神经影像解剖及血供范围分布图-颅脑CT/MR【矢状位】
神经影像解剖及血供范围分布图-颅脑CT【轴位】
查看更多